Single sign-on overview
Single sign-on (SSO) lets users access Docker by authenticating through their identity providers (IdPs). SSO can be configured for an entire company, including all associated organizations, or for a single organization that has a Docker Business subscription.
How SSO works
When SSO is enabled, Docker supports a non-IdP-initiated flow for user sign-in. Instead of signing in with a Docker username and password, users are redirected to your IdP’s sign-in page. Users must initiate the SSO authentication process by signing in to Docker Hub or Docker Desktop.
The following diagram illustrates how SSO operates and is managed between Docker Hub, Docker Desktop, and your IdP.
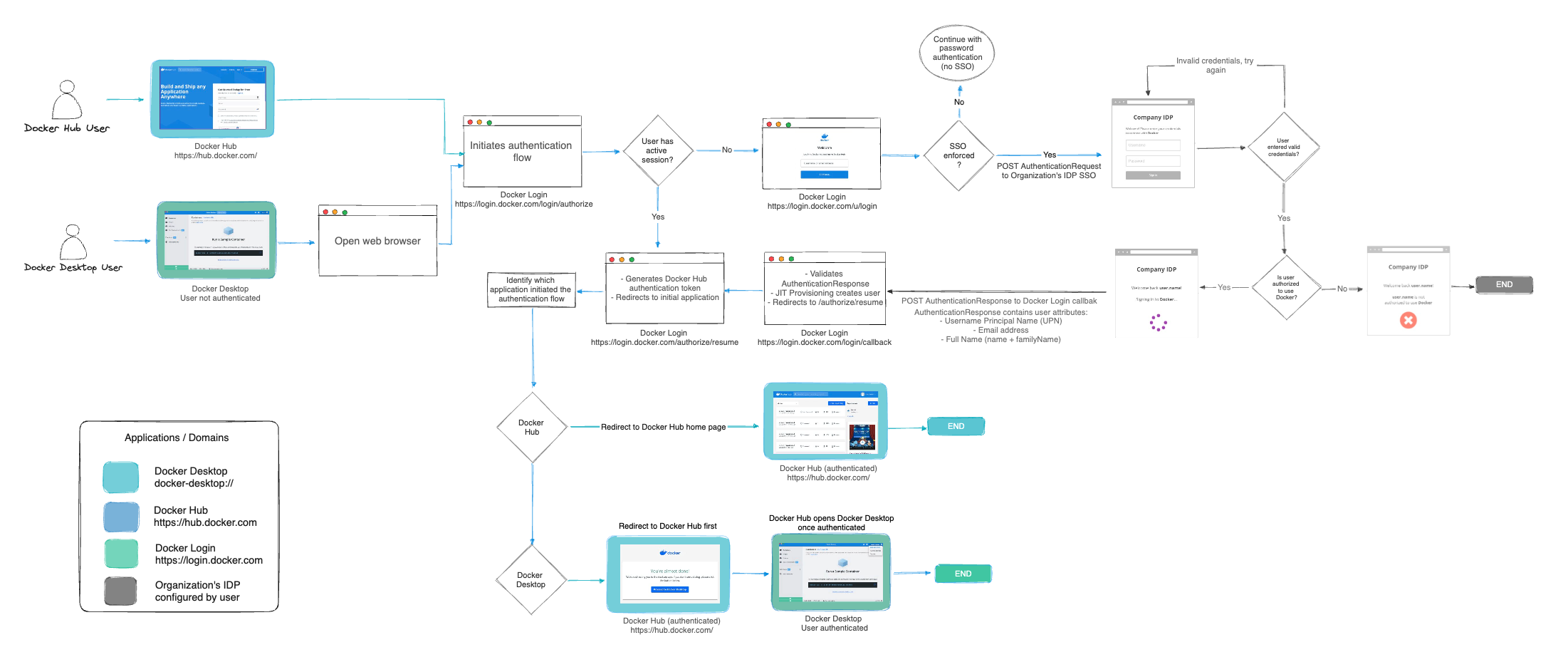

Set up SSO
To configure SSO in Docker, follow these steps:
- Configure your domain by creating and verifying it.
- Create your SSO connection in Docker and your IdP.
- Link Docker to your identity provider.
- Test your SSO connection.
- Provision users in Docker.
- Optional. Enforce sign-in.
- Manage your SSO configuration.
Once configuration is complete, users can sign in to Docker services using their company email address. After signing in, users are added to your company, assigned to an organization, and added to a team.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure the following conditions are met:
- Notify your company about the upcoming SSO sign-in process.
- Ensure all users have Docker Desktop version 4.42 or later installed.
- Confirm that each Docker user has a valid IdP account using the same email address as their Unique Primary Identifier (UPN).
- If you plan to enforce SSO, users accessing Docker through the CLI must create a personal access token (PAT). The PAT replaces their username and password for authentication.
- Ensure CI/CD pipelines use PATs or OATs instead of passwords.
ImportantDocker plans to deprecate CLI password-based sign-in in future releases. Using a PAT ensures continued CLI access. For more information, see the security announcement.
Next steps
- Start configuring SSO.
- Read the FAQs.
- Troubleshoot SSO issues.